Variables, Conditionals and Exercises
Java 101 - Class 1
What we want to achieve
Exercises
Debugging
תנאי מקוצר - ternary conditional operator
MyConsole and Scanner
compilation and runtime errors
compiling and running via cmd/terminal
טבלת מעקב (מצגות)
What we learnt in class
חשבון ומודלו
if and if-else
printing to screen
System.out.printlnwhile
Interger.MAX_VALUE
המרת מספרים מממשי לבינראי ולהיפך
Exercises
I0 - קלט ופלט
פלט נעשה ע"י הפקודה
ברוב הide נוכל לכתוב syso או sout כדי שהide ישלים אותנו אוטומטית
בקלט יש לנו 2 דרכים
Scanner
MyConsole (מה שלמדים בהתחלה בשיעור)
MyConsole
Scanner
input:
output:
Variables
משתנים פרימיטיבים

if and if else
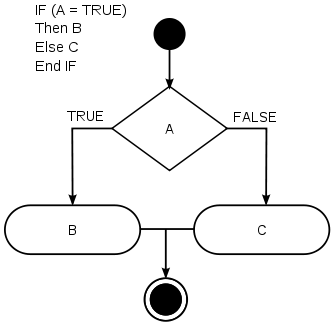
תרגיל: תנאים
Given an integer n , perform the following conditional actions:
If n is odd, print
StrangeIf n is even and in the inclusive range of 2 to 5 , print
Not StrangeIf n is even and in the inclusive range of 6 to 20, print
StrangeIf n is even and greater than 20, print
Not Strange
Solution
תרגיל: האם זה שנה מעוברת
כתבו תוכנית המחזיר האם השנה הוא שנה מעוברת או לא
To determine whether a year is a leap year, follow these steps:
If the year is evenly divisible by 4, go to step 2. Otherwise, go to step 5.
If the year is evenly divisible by 100, go to step 3. Otherwise, go to step 4.
If the year is evenly divisible by 400, go to step 4. Otherwise, go to step 5.
The year is a leap year (it has 366 days).
The year is not a leap year (it has 365 days).
examples:
1600 ✔️ leap year
1700 ❌ not leap year
1800 ❌ not leap year
1900 ❌ not leap year
2000 ✔️ leap year
2001 ❌ not leap year
2004 ✔️ leap year
בא עכשיו לגרום לתוכנית לא להפסק
כמו שניתן לשים לב, עטפנו את התוכנית שלנו עם while
שים לב שמנו את Scanner בחוץ ככה לא נצטרך פעם לייצר משתנה חדש כל פעם. בנוסף גם הסגירה שלו בחוץ
תרגילים: המרות
מה יהיה הפלט?
שאלו את עצמכם למה ההדפסה הראשונה יוצא 1.0 🤔
מה יהיה הפלט?
מה יהיה הפלט?
כאן הכזרנו על 3 משתני float
לולי היינו עושים ככה הקוד לא מתקפל
לא היה מתקפל כי ה y היה double. לזה קוראים compilation error
Runtime Error
מאוחר יותר נלמד על try וcatch שיעזרו לנו להתמודד עם שגיאות
תרגיל
כתבו אם מספר הוא int, short or long
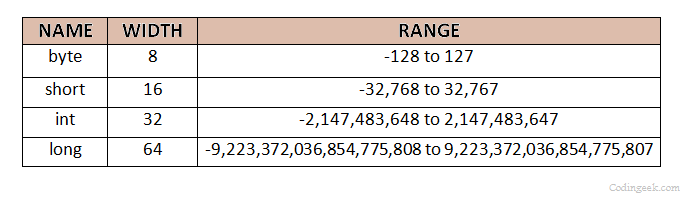
מספר שלם עובד לנו, אבל מה קורה במספר ממשי
קיבלנו Runtime error
על הדרך בא נוסיף גם while ככה שכל עוד הקלט אינו 0 הוא ימשיך לבקש
גם היינו יכול לעשות
&& ((short) n) == nו((int) n) == nבתנאייש לזה ביצועים יותר גבוההים
Last updated