Lesson 9 - More OOP
DIY - Creating Fib Class (10 minutes)
Solution
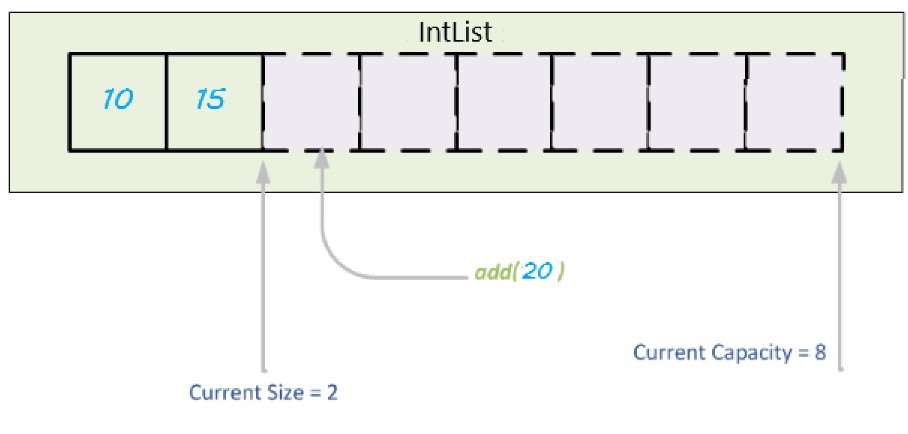
Creating an IntList
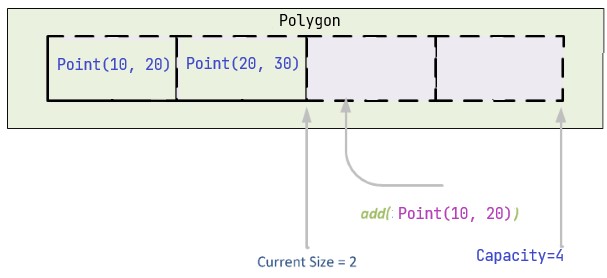
Polygon (Point list)

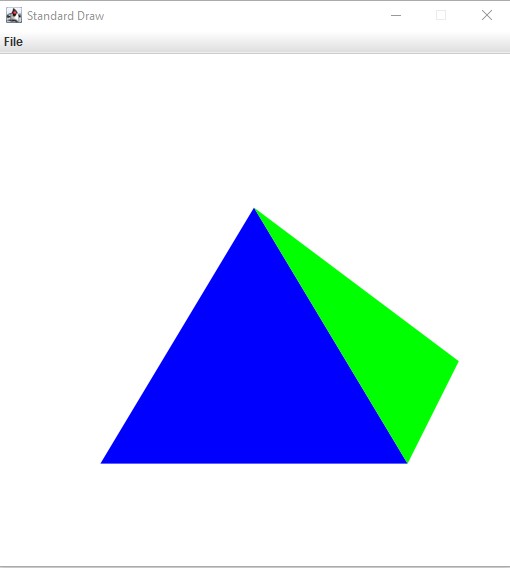
Drawing the polygon
Last updated







Last updated
Fib fib = new Fib();
fib.next(2);
System.out.println(fib);
System.out.println(fib.next(3));
System.out.println(fib.next().next());
Fib fib2 = new Fib(7).next().prev();
System.out.println(fib2);
System.out.println("are fibs equal? " + (fib.equals(fib2) ? "yes" : "no"));Fib(2) = 3
Fib(5) = 13
Fib(7) = 34
Fib(7) = 34
are fibs equal? yespublic class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fib fib = new Fib();
fib.next(2);
System.out.println(fib);
System.out.println(fib.next(3));
System.out.println(fib.next().next());
Fib fib2 = new Fib(6).next();
System.out.println(fib2);
System.out.println("are fibs equal? " + (fib.equals(fib2) ? "yes" : "no"));
}
}public class Fib {
private int a;
private int b;
private int n;
Fib() {
this(0); // call: Fib(int num), don't increment
}
Fib(int num) {
a = 0;
b = 1;
n = 0;
next(num);
}
Fib next() {
return next(1);
}
Fib next(int num) {
while (num > 0){
int temp = a;
a = b;
b += temp;
--num;
++n;
}
return this;
}
Fib prev() {
return prev(1);
}
Fib prev(int num) {
while (num > 0 && n > 1){
int temp = a;
a = b - a;
b = temp;
--num;
--n;
}
return this;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Fib(" + n + ") = " + (a+b) ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Fib fib = (Fib) o;
return n == fib.n;
}
}Fib(2) = 3
Fib(5) = 13
Fib(7) = 34
Fib(7) = 34
are fibs equal? yespublic class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntList list = new IntList(4, 10);
list.add(20).add(30);
System.out.println(list);
for (int i = 0; i < list.length() ; i++)
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ,");
System.out.println("\n======= Equals =======\n");
IntList new_list = new IntList(list); // Calls copy constructor
System.out.println("new_list: " + new_list.toString());
System.out.println("are the list the same: " + new_list.equals(list));
new_list.add(100);
System.out.println("new_list: " + new_list);
System.out.println("are the list the same: " + new_list.equals(list));
new_list.remove_index(6);
System.out.println("new_list: " + new_list);
System.out.println("are the list the same: " + new_list.equals(list));
}
}import java.util.Arrays;
public class IntList {
private int size = 0; // shouldn't be public
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private int[] elements;
// ===== Constructors =====
//default constructor
public IntList() {
elements = new int[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]; // or: this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY)
}
// Create int list with x elements, no values
public IntList(int size) {
elements = new int[size];
}
// Create int list with x elements, no values
public IntList(int size, int num_2_fil) {
elements = new int[size];
this.size = size;
Arrays.fill(elements, num_2_fil);
}
// copy constructor
public IntList(IntList other) {
size = other.size;
elements = new int[size];
//deep copy, could also use:
//elements = Arrays.copyOf(other.elements, other.size);
for (int i = 0; i < other.length(); i++)
elements[i] = other.elements[i]; // or other.add(elements[i])
}
// ===== methods =====
//add elemements
public IntList add(int elem) {
if (size == elements.length) {
increaseCapacity();
}
elements[size++] = elem;
return this; //<--------- show without returning this
}
//add elemements
public IntList add(int elem, int amount) {
while (amount>=0){
if (size == elements.length)
increaseCapacity();
elements[size++] = elem;
--amount;
}
return this; //<--------- show without returning this
}
//double the capacity
private void increaseCapacity() {
int newSize = elements.length * 2;
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, newSize);
}
//get index
public int get(int i) {
if (i>= size || i <0)
return -1;
return elements[i];
}
public int length() {
return size;
}
//remove index
public int remove_index(int index) {
int removed_elem;
if (index>= size || index <=0)
return -1;
removed_elem = elements[index];
size--;
//end of IntList
if (index==elements.length-1){
elements[index] = 0;
}
for (int i = index; i < elements.length; i++)
if (i+1<elements.length)
elements[i] = elements[i+1];
return removed_elem;
}
// ===== toString & equals =====
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder elems = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++)
elems.append(elements[i] + ", ");
elems.append(elements[size-1] + "]");
return "IntList{" +
"size=" + size +
", capacity=" + elements.length +
", elements=" + elems.toString() +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
IntList intList = (IntList) o;
if (size == intList.size){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elements[i] != intList.get(i))
return false;
return true;
}
return false;
// return size == intList.size
// && Arrays.equals(elements, intList.elements);
}
}IntList{size=6, capacity=8, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 30]}
10 ,10 ,10 ,10 ,20 ,30 ,
======= Equals =======
new_list: IntList{size=6, capacity=6, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 30]}
are the list the same: true
new_list: IntList{size=7, capacity=12, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 30, 100]}
are the list the same: false
new_list: IntList{size=6, capacity=12, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 20, 30]}
are the list the same: truepublic class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntList list = new IntList(4, 10).add(20);
System.out.println(list);
list.add(100,4).remove_index(4);
System.out.println(list);
}
}IntList{size=5, capacity=8, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 20]}
IntList{size=9, capacity=16, elements=[10, 10, 10, 10, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100]}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Polygon list = new Polygon(3, new Point(1, 2)).add(new Point(30, 40));
System.out.println(list);
list.add(new Point(-100, -100),3).remove_index(4);
System.out.println(list);
Polygon new_list = new Polygon(list);
System.out.println("are the Polygons the same? " + list.equals(new_list));
list.remove_index(3);
System.out.println("are the Polygons the same? " + list.equals(new_list));
}
}import java.util.Arrays;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Polygon {
private int size = 0; // shouldn't be public
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private Point[] elements;
private Color color;
private String name = new String("");
// ===== Constructors =====
//default constructor
public Polygon() {
this(DEFAULT_CAPACITY); //call Polygon(int size);
}
// Create Polygon with x elements, no values
public Polygon(int size) {
elements = new Point[size];
setColor(0,0,255);
}
// Create int Polygon with x elements, no values
public Polygon(int size, Point point_2_fil) {
elements = new Point[size];
this.size = size;
Arrays.fill(elements, point_2_fil);
setColor(0,0,255);
}
// copy constructor
public Polygon(Polygon other) {
size = other.size;
elements = new Point[size];
color = other.color;
for (int i = 0; i < other.length(); i++)
elements[i] = other.elements[i]; // or other.add(elements[i])
}
// ===== methods =====
private double[] convert2DoubleArray(String x_or_y) {
double[] list = new double[elements.length];
switch (x_or_y) {
case "x":
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
list[i] = elements[i].getX();
return list;
//break;
case "y":
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
list[i] = elements[i].getY();
return list;
default:
return new double[]{0., 0.};
}
}
public void setColor(int r, int g, int b) {
this.color = new Color(r, g, b);
}
public void draw() {
StdDraw.setPenColor(color);
StdDraw.filledPolygon(convert2DoubleArray("x"), convert2DoubleArray("y"));
}
//add elemements
public Polygon add(Point elem) {
if (size == elements.length) {
increaseCapacity();
}
elements[size++] = elem;
return this; //<--------- show without returning this
}
//add elemements
public Polygon add(Point elem, int amount) {
while (amount>=0){
if (size == elements.length)
increaseCapacity();
elements[size++] = elem;
--amount;
}
return this; //<--------- show without returning this
}
//double the capacity
private void increaseCapacity() {
int newSize = elements.length * 2;
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, newSize);
}
//get index
public Point get(int i) {
if (i>= size || i <0)
return new Point();
return elements[i];
}
public int length() {
return size;
}
//remove index
public Point remove_index(int index) {
Point removed_elem;
if (index>= size || index <=0)
return new Point();
removed_elem = elements[index];
size--;
//end of Polygon
if (index==elements.length-1){
elements[index] = new Point();
}
for (int i = index; i < elements.length; i++)
if (i+1<elements.length)
elements[i] = elements[i+1];
return removed_elem;
}
// ===== toString & equals =====
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder elems = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size-1; i++)
elems.append(elements[i] + ", ");
elems.append(elements[size-1] + "]");
return "Polygon{" +
"size=" + size +
", capacity=" + elements.length +
", elements=" + elems.toString() +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Polygon polygon = (Polygon) o;
if (size == polygon.size){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (elements[i] != polygon.get(i))
return false;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}class Point {
private double x, y;
//=== constructors ===
//default constructor
Point() {
x =0;
y = 0;
}
Point(double new_x, double y) {
x = new_x;
this.y = y;
}
//copy constructor
Point(Point p) {
x = p.x; // Since this is the same class I can access without getter/setter
y = p.y;
}
//=== static methods ===
public static double distance(Point a, Point b) {
double dist = Math.pow(a.x-b.x, 2) + Math.pow(a.y-b.y, 2);
return Math.sqrt(dist);
}
//=== getters and setters ===
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public String toString() {
return "Point {" + " x=" + x + ", y=" + y + " }";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Point point = (Point) o;
return Double.compare(point.x, x) == 0 && Double.compare(point.y, y) == 0;
}
}PointList{size=4, capacity=6, elements=[Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=30.0, y=40.0 }]}
PointList{size=7, capacity=12, elements=[Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=1.0, y=2.0 }, Point { x=30.0, y=40.0 }, Point { x=-100.0, y=-100.0 }, Point { x=-100.0, y=-100.0 }, Point { x=-100.0, y=-100.0 }]}
are the Polygons the same? true
are the Polygons the same? false double[] x = { 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.2 };
double[] y = { 0.2, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1 };
StdDraw.filledPolygon(x, y);private double[] convert2DoubleArray(String x_or_y) {
double[] list = new double[elements.length];
switch (x_or_y) {
case "x":
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
list[i] = elements[i].getX();
return list;
//break;
case "y":
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
list[i] = elements[i].getY();
return list;
default:
return new double[]{0., 0.};
}
}public class Main {
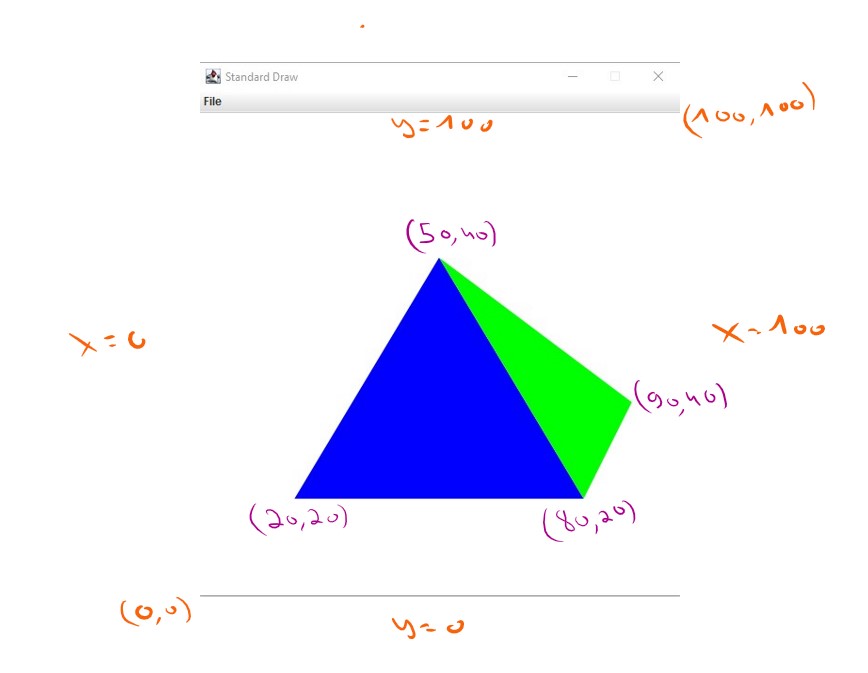
public static void main(String[] args) {
Polygon polygon1 = new Polygon();
polygon1.add(new Point(20,20));
polygon1.add(new Point(80,20));
polygon1.add(new Point(50,70));
polygon1.add(new Point(20,20));
Polygon polygon2 = new Polygon();
polygon2.setColor(0,255,0);
polygon2.add(new Point(80,20));
polygon2.add(new Point(90,40));
polygon2.add(new Point(50,70));
polygon2.add(new Point(80,20));
StdDraw.setXscale(0, 100);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, 100);
polygon1.draw();
polygon2.draw();
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Polygon[] polygons = new Polygon[3];
polygons[0] = new Polygon();
polygons[0].add(new Point(229,153));
polygons[0].add(new Point(160,218));
polygons[0].add(new Point(177,325));
polygons[0].add(new Point(249,268));
polygons[0].add(new Point(229,153));
polygons[1] = new Polygon();
polygons[1].setColor(0,255,0);
polygons[1].add(new Point(249,268));
polygons[1].add(new Point(177,325));
polygons[1].add(new Point(269,336));
polygons[1].add(new Point(349,283));
polygons[1].add(new Point(249,268));
polygons[2] = new Polygon().setName("redPolygon");
polygons[2].setColor(255,0,0);
polygons[2].add(new Point(349,283));
polygons[2].add(new Point(328,182));
polygons[2].add(new Point(229,153));
polygons[2].add(new Point(249,268));
polygons[2].add(new Point(349,283));
StdDraw.setXscale(0, 500);
StdDraw.setYscale(0, 500);
for (int i = 0; i < polygons.length; i++) {
polygons[i].draw();
System.out.println(polygons[i]);
}
}
}polygon_1: Polygon{num of points: 5, capacity=10, elements=[Point { x=229.0, y=153.0 }, Point { x=160.0, y=218.0 }, Point { x=177.0, y=325.0 }, Point { x=249.0, y=268.0 }, Point { x=229.0, y=153.0 }]}
polygon_2: Polygon{num of points: 5, capacity=10, elements=[Point { x=249.0, y=268.0 }, Point { x=177.0, y=325.0 }, Point { x=269.0, y=336.0 }, Point { x=349.0, y=283.0 }, Point { x=249.0, y=268.0 }]}
redPolygon: Polygon{num of points: 5, capacity=10, elements=[Point { x=349.0, y=283.0 }, Point { x=328.0, y=182.0 }, Point { x=229.0, y=153.0 }, Point { x=249.0, y=268.0 }, Point { x=349.0, y=283.0 }]}