Multidimensional arrays & Functions
Lecture 5 - Multidimensional arrays & Functions
Functions
public class Main {
public static void printMe(int value_of_num) {
System.out.println(value_of_num);
value_of_num = 99;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 5;
printMe(num);
printMe(num);
}
}Exercise: Palindrome

Multidimensional arrays



Exercise: print the matrix and its sum
Explanation:
Exercise: Trace of matrix

Exercise: Transpose
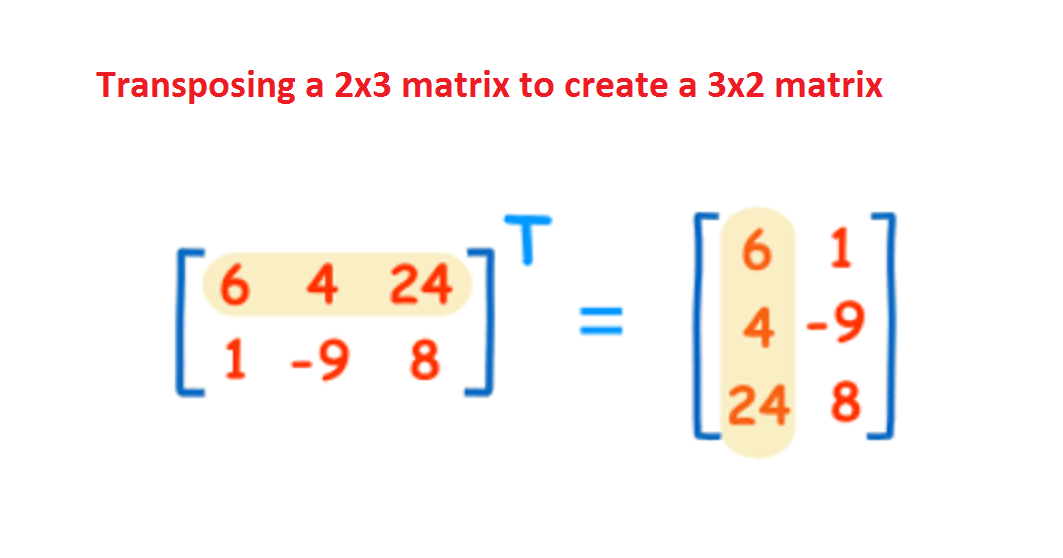
Exercise: Check Symmetry of matrix


Matrix Multiplication

Last updated