Linked Lists
Lesson 11
Last Week
This week
Scanner
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int my_int = scan.nextInt();
double my_double = scan.nextDouble();
String my_str = scan.next();
System.out.println("int:" + my_int);
System.out.println("double:" + my_double);
System.out.println("string:" + my_str);
scan.close();
}
}LinkedList
advantages of LinkedList
disadvantage of LinkedList
Basic implementation
Test Exercise: Add to an ordered Linked List

Solution:
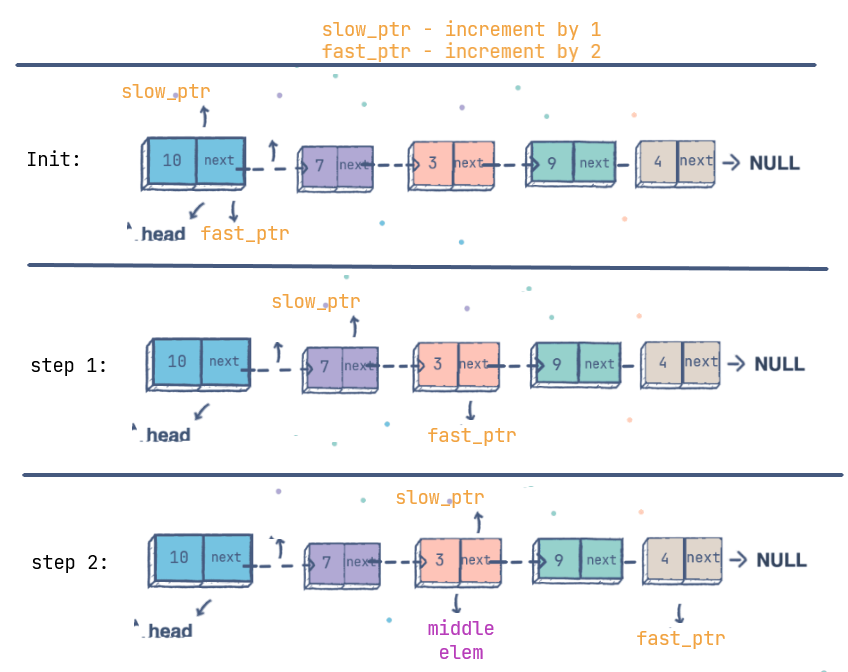
Exercise: Find the middle element (position) of LinkedList
Solution
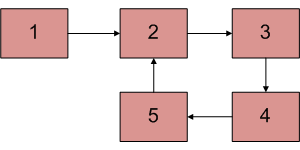
Test Exercise: Cycle in LinkedList

Solution
But how do we remove the the cycle?
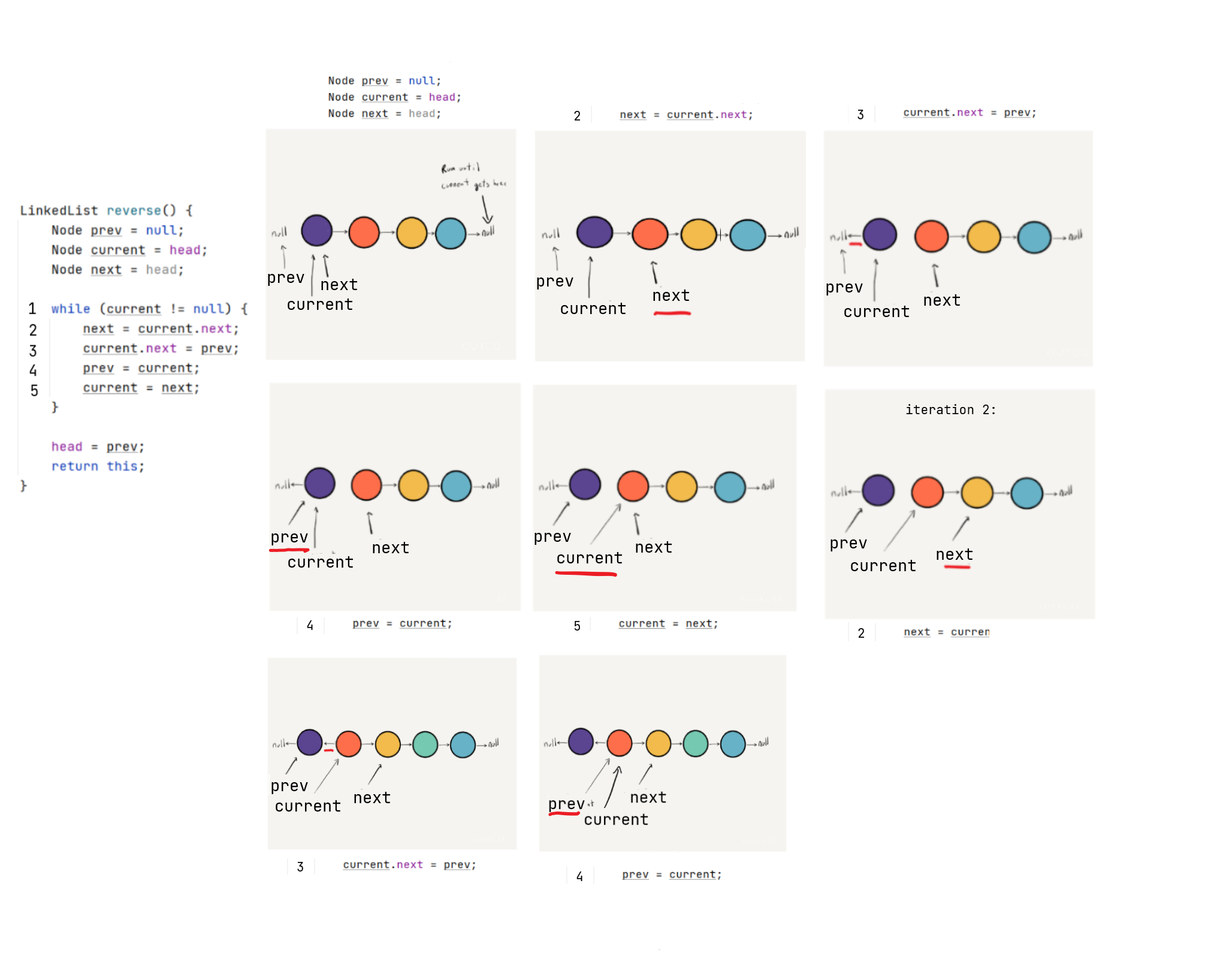
Exercise: Reverse LinkedList - Iteratively- DIY (15 minutes)
Solution
Exercise: Reverse LinkedList - Recursively
solution
Exercise: Partition LinkedList
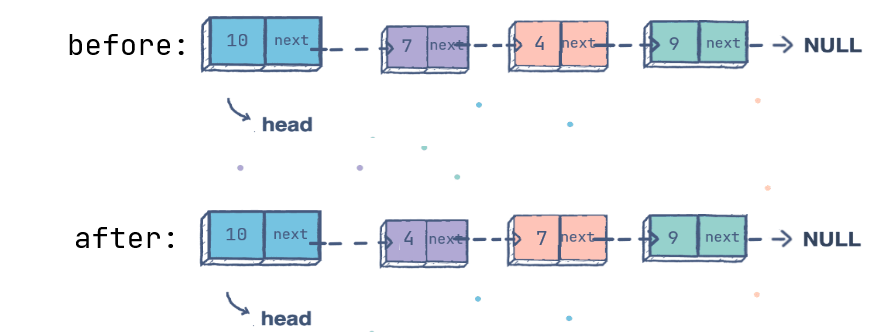
Solution
Doubly LinkedList
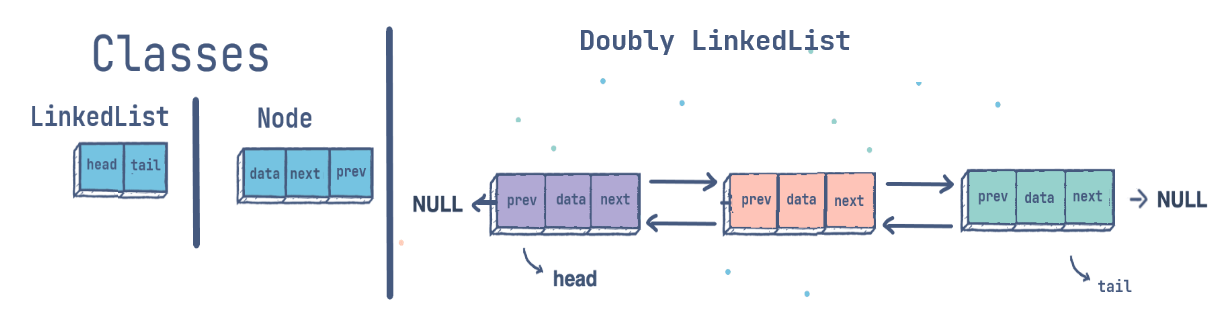
Advantages over singly linked list
Disadvantages over singly linked list
Last updated